|
Various Infections - Anti-Infectives in Clinical
Usage
(F 25 - F 42)
|
|
F
25
BRUCELLOSIS
IN THE COUNTY OF TRIKALA
T.K.
Galeas, A. Papadopoulos, S. Mylonas, V. Galea, K. Ranellou,
E. Militsi, M. Lemoni
B’ Internal Medicine of Trikala, Microbiology Laboratory,
General Hospital of Trikala, Greece
The
purpose of the work is to show the incidence of brucellosis
(an animal transmitted disease caused by brucella) in man
the last 30 years in the county of Trikala.
Patients-Method:
From the hospital files we wrote down the patients admitted
the last 30 years with brucellosis. We divided these 30
years in six five-year periods with the exception of 1995-1997
period when files had been destroyed by flood.
Results:
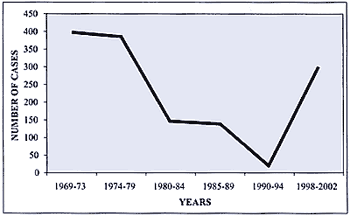
In a total number of 1387 patients with brucellosis we had
1969-73: 400, 1974-79: 388, 1980-84: 144, 1985-89: 140,
1990-94: 17, 1998-2002: 300.
In 1975
a project was applied for the extinction of the disease
in animals and consequently in man but for some reasons
it was interrupted.
In
conclusion: Brucellosis had been decreased for some
years.
However the incomplete application of brucellosis extermination
programme had as a result the increase of brucellosis in
man in the levels of 30 years ago.
|
|
|
F
26
POLYMORPHIC
GENES OF TNF-alpha AND IL-8 IN PATIENTS WITH HELICOBACTER
PYLORI-INDUCED PEPTIC ULCER
Y.
Mándi, Z. Gyulai, G. Klausz, A. Tiszai, J. Lonovics
Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunobiology, 1st
Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University
Szeged, Hungary
Background:
Activation of inflammatory cytokines plays an important
role in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer. The aim of this
study was to investigate the TNF-alpha and IL-8 levels in
gastric biopsy samples of ulcer patients. Since cytokine
production is often determined by the nucleotide polymorphisms
of cytokine genes, we investigated the relationship of the
TNF-alpha and IL-8 polymorphisms and the development of
H. pylori-induced duodenal ulcer.
Methods:
Gastric biopsy samples from 40 H. pylori positive
duodenal ulcer (DU) patients were used for determination
of local cytokine production by ELISA. DNA from 80 H.
pylori positive DU patients were used for genetical
experiments. The -308 polymorphism of TNF-alpha gene was
determined by NcoI RFLP, and the polymorphism for IL-8 –
251 by ARMS methods. DNA isolated from healthy blood donors
(n=50) served as controls.
Results:
The production of TNF-alpha and IL-8 was significantly higher
(p < 0.001) in antral mucosa in DU patients than in H.
pylori negative subjects (n=12). A significant difference
however could not be observed in TNF-alpha -308 polymorphism
between ulcer patients and the healthy controls. In contrast,
allelic frequencies proved to be higher (72%) for the IL-8
–251 A allele, resulting in a significant overproduction
of IL-8.
Conclusion:
Host factors play an important role in H. pylori-induced
ulcer. TNF-alpha and IL-8 production are increased after
H. pylori infection. Analysis of genetic predisposition
for enhanced cytokine production resulted in a significant
association only for the IL-8 polymorphism.
|
|
|
F
27
AN
EXOTIX CASE OF PNEUMONIA
M.
Széll, H. Laferl, H. Pichler
4th Medical Department with Infectious Diseases and Tropical
Medicine
Kaiser-Franz-Josef-Hospital, Vienna, Austria
We present
a case of a 73-year-old woman with severe pneumonia on return
from a 4-month stay on Fiji Islands.
The patient had spent the winter months on Viti Levu island
where her daughter is living. Two days after returning to
Vienna in January 2002 she developed severe watery diarrhea
(up to 30 bowel movements daily) without nausea, vomiting
or abdominal pain. In the following days her general condition
deteriorated with extreme fatigue and fainting. Her general
practitioner diagnosed “rhythm problems” due to
exsiccosis and she was referred to our intermediate care
unit.
On admission she was afebrile (temperature, however, rose
to 38.4°C within 12 hours), had tachypnoea with bilateral
rhonchi and blood gas analysis revealed partial respiratory
insufficiency. Chest X-ray showed bilateral infiltrates.
ECG confirmed atrial fibrillation. Laboratory investigations
showed leukocytosis and marked elevations of C-reactive
protein, liver enzymes and creatinkinase. Severe community
acquired pneumonia was diagnosed and an empiric antibiotic
treatment with cefuroxime and clarithromycin was started.
Urinary antigen tests for pneumococci and legionella were
negative. Multiple blood cultures showed no growth. Serological
testing for rickettsia, chlamydia and mycoplasma did not
yield any positive results. There were, however, high IgM
and IgG antibody titers against leptospira. Antibiotic treatment
was changed to oral doxycycline. The patient recovered slowly
and was discharged in good condition after 18 days. She
recalled close contact to healthy pet cats during her stay
on Fiji but not to any rodents.
Conclusion:
In patients with pneumonia on return from tropical countries
leptospirosis should be ruled out.
|
|
|
F
28
PHARMACODYNAMIC
TARGET ATTAINMENT ANALYSIS AGAINST STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE
USING LEVOFLOXACIN 500 MG AND 750 MG ONCE DAILY IN HOSPITALIZED
PATIENTS WITH COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA
A.
Noreddin, T. Marras, C. Chan, D. Hoban, G. Zhanel
University of Manitoba, Medical Microbiology, Winnipeg,
Canada;
University of Toronto, University Health Network, Toronto,
Canada
Objective:
This work aimed at simulating pharmacodynamic target attainment
potential against Streptococcus pneumoniae using
levofloxacin 500 mg and 750 mg once daily in hospitalized
patients with community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
Methods:
Pharmacokinetic simulations of susceptibility data with
S. pneumoniae from our ongoing national surveillance
study (Canadian Respiratory Organism Susceptibility Study-CROSS)
were used to produce pharmacodynamic indices of AUC0-24/MIC90.
Monte Carlo simulations were then used to analyze target
attainment of levofloxacin using doses of 500 mg and 750
mg once daily to achieve free drug AUC0-24/MIC90
of 30 for. S. pneumoniae in patients with CAP.
Results:
Pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin simulated after both 500
mg and 750 mg doses resulted in levofloxacin clearance:
elderly patients < immunocompromised patients < young
patients = healthy volunteers. Levofloxacin t 1/2 values
were the longest in elderly patients (14.7 - 8.5 h) as well
as immunocompromised patients (13.0 - 10.1 h), while young
patients with CAP (8.9 - 5.8 h) had a slightly longer t
1/2 than healthy volunteers (7.4 - 0.9 h). Free levofloxacin
AUC0-24 as well as AUC0-24/MIC90
for S. pneumoniae were highest in elderly patients
followed by immunocompromised patients > young patients
> volunteers. Monte Carlo simulation using levofloxacin
500 mg yielded probabilities of achieving free-drug AUC0-24/MIC90
of 30 at 95.9%, 83.8%, 71.9% and 78.5% for elderly patients,
immunocompromised patients, young patients and healthy volunteers,
respectively.
Conclusion:
Using levofloxacin 750 mg, the probability of achieving
free-drug AUC0-24/MIC90 of 30 was
98.5%, 96.4%, 89.5% and 93.3% for elderly patients, immuno-compromised
patients, young patients and healthy volunteers, respectively.
We conclude that levofloxacin pharmacokinetics in elderly
patients with CAP are markedly different than those of young
patients or healthy volunteers. Higher levofloxacin AUC
and longer t 1/2 values in elderly patients with CAP compared
to healthy volunteers provide better pharmacodynamic parameters
(free-Drug AUC0-24/MIC) leading to higher probability of
pharmacodynamic target attainment and improved bacteriological
outcome against S. pneumoniae.
|
|
|
F
29
ANTIBIOTICS
IN HOME FIRST-AID SETS
S.K.
Zenkova, V.M. Semenov, V.V. Skvortsova, T.I. Dmitrachenko
Vitebsk State Medical University, Republic Belarus
One
of the most important ways of the development of antibiotic
resistance is the overusage of antibiotics by the patients.
To assess the level of antibiotics abuse we have investigated
the content of home first-aid sets of 186 families living
in Vitebsk, Minsk, Bobruysk and Molodechno.
We have revealed that 144 (77.4%) of all interviewed families
had some kind of antibiotics in their home first-aid set.
The quantity of antibiotics was 1-7, and 11.7% of it were
of expired date but, according to respondents opinion, they
were fit for use. The most frequent were ampicillin (77.8%),
erythromycin (30.5%), tetracycline (29.1%), co-trimoxazol
(27.8%), doxycyclin (27.8%), chloramphenicol (22.2%).
Only 4.17% of families applied antibacterial preparations
according to the prescriptions of their physicians. Only
22.2% of people interviewed knew the correct indications
for usage of antibacterial preparations from their first-aid
set, 30% didn’t know these indications, and 30.5% of
respondents knew the indications partially. There was no
sufficient difference between urban and rural population
in the patterns of incorrect usage of antibiotics. 37.3%
of families having children gave the incorrect answers concerning
the usage of antibiotics in children.
According to respondents opinion, the main indications for
the antibiotics application are any increase of temperature,
rhinitis, cough or stomachache. The majority of them used
antibiotics irregularly, 1-2 times a day for 1-3 days.
Our analysis indicates wide uncontrolled application of
antibiotics by the population what may be a possible cause
for increasing antibiotic resistance of bacteria. To solve
this problem it is necessary to prohibit selling antibiotics
without prescription.
|
|
|
F
30
Analysis
of the prevalence and RFLP subtyping of Borrelia burgdorferi
sensu lato (Bb) in Ixodes ricinus ticks from an endemic
area in Austria
M.
Glatz, V. Fingerle, B. Wilske, R.R. Müllegger
Department of Dermatology, Univ. Graz, Austria
Objective:
(i) To determine the prevalence of Bb in Ixodes ricinus
ticks in an highly endemic area for tick-transmitted diseases
in Austria (city of Graz) by PCR.
(ii) To identify the borrelia genotypes present in those
ticks by RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism)
analysis.
Methods:
131 ticks were collected in June 2002 by the flagging method
in a woodland recreation area of Graz. All ticks were placed
into humidified tubes and stored at 4°C until separate
DNA extraction for each tick with a commercial preparation
kit (Roche). Extracted DNA was analysed using a semi-nested
PCR with 2 primer pairs specific for an 818 bp fragment
of the Bb ospA gene to detect infection of ticks followed
by RFLP analysis with 5 endonucleases for genotype identification
of positive samples.
Results:
27/131 (21%) ticks were found to be positive for Bb, 14
of which were nymphs and 13 were adults. RFLP analysis revealed
18 (67%) ticks to be infected with the genotype B. afzelii,
5 (19%) with Bb s.s., 3 (11%) with B. garinii,
and 1 (3%) with B. valaisiana.
Conclusion:
(i) A high percentage of ticks in Graz is infected with
Bb.
(ii) Tick nymphs have the potential to transmit Bb.
(iii) B. afzelii is the most prevalent genotype and
Bb s.s. is found more frequently than expected.
(iv) B. valaisiana was detected for the first time
in Austria in this study.
|
|
|
F
31
MIDECAMYCIN
IN TREATMENT OF CHRONIC UROGENITAL CHLAMIDIOSIS
V.M.
Kozin, A.N. Gorodovich
Vitebsk State Medical University, Republic Belarus
We have
studied the clinical efficiency of midecamycin application
in 23 patients ill with chronic urogenital chlamidiosis
aged 19-54 (16 men and 7 women). In male patients there
were the signs of anterior urethritis (4), total urethritis
(7) and urethroprostatitis (5). In female patients we have
revealed the signs of urethritis and cervicitis, and also
subacute endometritis and parametritis (2). The majority
of patients had different complaints as itch, small pain
during the emiction, genital discomfort. Some patients had
perineum and femoral aches. All patients had positive results
of immunofluorescence reaction (IFR) for the chlamidia antigens
made in scraping smears. All patients were treated with
injections of midecamycin (400 mg 3 times a day). We have
also prescribed enterol with the aim of biocorrection (250
mg 2 times a day). Female patients were recommended to introduce
anti-candidosis drugs into vagina.
We assessed the dynamics of the symptoms for the time of
treatment. The control of cure was made in 1, 2 and 3 months
from the last day of treatment. All patients overcame the
injections well. We haven’t seen any cases of intolerance.
Finally, all patients became symptoms-free, including women
suffering from endometritis and parametritis. We haven’t
found chlamidia in urethra smears of 15 men using IFR. Chlamidia
was also eliminated in 6 women including suffering from
endometritis and parametritis.
Thus, application of midecamycin in a complex treatment
of patients with chronic urogenital chlamidiosis results
in full clinical and microbiological cure in 89% of patients.
|
|
|
F
32
FIBRONECIN
IN ACUTE AND CHRONIC HEPATITIS B
P.
Khaykin
Dnepropetrovsk Medical Academy,Ukraine
Objectives:
The aim of the research was to carry out a comparative analysis
of free and combined with circulated immune complexes (CIC)
fibronectin (FN) contents in acute and chronic hepatitis
B.
Methods:
57 patients with acute hepatitis B (1 group), 32 patients
with chronic hepatitis B (2 group) and 30 healthy persons
were investigated. The parameters were determined in plasma
at the first day of stay in the hospital and 1 month later.
Contents of free and combined FN were determined using ELISA,
FN degradation products – using Western Blot with the
rabbit antibodies to FN, level of CIC – using precipitation
with 3% PEG 6000. Results in acute hepatitis B the average
contents of free FN was higher than in control group and
chronic patients (t=6.93; p < 0.001; t=8.63; p < 0.001).
Lowering of free FN contents was observed in dynamic (t
= 5.23; p < 0.001). The level of CIC at the first investigation
in both groups exceeded such in a control group (t = 6.14;
p < 0.001; t = 5.11; p < 0.005). In acute hepatitis
B the lowering of a CIC level (t = 3.92, p < 0.01) was
observed. It was determined that concentration of combined
FN was higher in acute hepatitis patients than in control
group and chronic hepatitis (U = 83.2; p < 0.05; U=68.3;
p < 0.05). We detected products of a combined FN degradation
in the majority of the chronic hepatitis B patients, in
1 group – less than for half of patients and in control
group only in 1/6.
Conclusion:
1. In patients with acute hepatitis B the contents of free
and combined FN increase in the beginning of disease and
decrease in the dynamics simultaneously with a level of
CIC.
2. In patients with chronic hepatitis reduced contents of
free and combined FN and degradation of combined FN are
observed.
|
|
|
F
33
LAMIVUDINE
IN SEVERE ACUTE VIRAL HEPATITIS
M.
Hurmuzache,V. Luca, O. Mihoc
UNIV. MED & PH, Iasi, Romania
Objective:
The aim of study is to show the effectiveness of lamivudine
in children aged under 16 with severe B acute viral hepatitis
(AVBH), including fulminant and subfulminant.
Methods:
Retroprospective study, comparing two groups of children
who were admitted in the Univ. Hosp. of Inf. Diseases, Iasi,
Romania, one of them between 1995-1998 (19 patients=group
A) who did not receive lamivudine and a second group (B=16
patients) admitted 1999-2002 who received 100 mg lamivudine,
daily. Each group was divided as follows: group A: A1 (13
severe AVBH), A2 (5 fulminant ac.B hep.) and A3 (1 subfulminant).
Group B: B1 (11 severe AVBH), B2 (4 fulminant), B3 (1 subfulminant).
Inclusion in one of these subgroups was decided in day 7
from admission for group A and according to the clinical
profile in the first day of lamivudine administration for
group B. Criteria to maintain patients in the study included
at least one of the next: symptomatology unchanged or worsened
for 10-14 days after admission, high levels of total bilirubin
(> 20 mg%), leuco/thrombopaenia, presence of haemorrhagic
syndrome (clinical+Quick < 35%), neurological signs.
Treatment with lamivudine was not begun before serological
diagnosis was established (IgM HBc +). Some of the patients
with fulminant hepatitis received also alpha interferon
(2 in groupA, 2 in group B). R=recovered, D=deaths.
Results:
Group A1 (13 patients, severe AVBH, lamivudine-): R=9 (69%),
D=4 (31%, evolution toward acute liver failure); group A2
(5 patients, fulminant hepatitis, lamivudine-): R=2 (40%),
D=3 (60%); 1 R and 1 D received also alpha interferon. Group
A3 (1 patient, subfulminant hepatitis, lamivudine-): R=1
(100%). Group B1 (11 patients, severe AVBH, lamivudine+):
R=10 (91%), D=1 (9%). Group B2 (4 patients, fulminant hepatitis,
lamivudine+): R=2 (50%), D=2 (50%). 1 R and 1 D received
also interferon alpha. Group B3 (1 patient, subfulminant
hepatitis, lamivudine+): R=1 (100%).
Conclusion:
As it can be observed, treatment with lamivudine significantly
reduces the number of severe acute B hepatitis with bad
evolution toward acute liver failure and sometimes death
(9% vs 31%) and improves mortality even in fulminant hepatitis,
so it should be administered immediately after clinical
or biological signs suggest an inadequate evolution.
|
|
|
F
34
APOPTOSIS/NECROSIS
INDUCED BY METAL COMPLEXES OF ACICLOVIR AND OF THIOSEMICARBAZONES
DURING HSV 1 INFECTION DEPENDS ON COMPLEX SPECIFICITIES
P.
Genova, T. Varadinova, P. Souza, D. Kovala-Demertzi, A.
Terron, A. Garcia-Raso, J. Fiol
Laboratory of Virology, Sofia University, Bulgaria; Universidad
Autonoma de Madrid, Spain; Universitat de les Illes Balears,
Palma de Mallorca; University of Ioannina, Ioannina, Greece
We previously
reported the activity of complexes of aciclovir (ACV) and
of thiosemicarbazones (pyridine-2-carbaldehyde - HFoTsc
and bis-benzyl-Tsc) of bivalent metal ions during HSV infection.
Here we present data on the effect of complexes of Zn(II),
Co(II), Cd(II), Ni(II), Pt(II), Pd(I) and Ag(I) on apoptosis
in HSV 1 infected and in noninfected MDBK cells. Apoptosis
was identified by morphological criteria using both fluorescent
acridine orange dye for DNA and Janus green B dye for mitochondria
staining. The following two sets of data were found: (i)
induction of apoptosis/necrosis by [Cd(ACV)Cl2].H2O,
[Ni(ACV)(NO3)]3.5H2O,
[Ni(ACV)2(H2O)4]Cl2.2ACV and Pd(II)
complexes of Tsc derivatives manifested by vesiculation
in the cytoplasm, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation
and clumping, as well as mitochondria condensation; (ii)
no induction of apoptosis/necrosis under the influence of
complexes of Zn(II), Co(II) and Ag(I) of ACV and of Pt(II)
of HFoTsc. These data are in accordance with those previously
published by other authors and confirm that the induction
of apoptosis/necrosis depends on the specificities of the
particular metal ion. Furthermore the induction of these
processes is independent on whether cells are infected by
HSV 1 or not.
(Project COST D20, 0006-01 and NSF, 1201)
|
|
|
F
35
USE
OF PREFORMING PHYSICAL FACTORS IN THE COMPLEX RESTORING
THERAPY OF CHILDREN WITH CHRONIC VIRAL HEPATITIS
O.V.
Kuznetsova, I.N. Fedchuk
Odessa State Medical University, Odessa, Ukraine
The
scope of the present work was to study the use of preforming
physical factors such as He-Ne laser irradiation with the
vacuum ultraphoresis of peloidin.
37 children with chronic viral hepatitis were under investigation
in the period of aggravation. The diagnosis was stated on
the basis of disease anamnesis and discrimination of hepatitis
viruses markers B and C. The patients obtained traditional
medicinal treatment accompanied by physiotherapy. The complex
restoring therapy included 6 daily applications of laser
bio-resonant irradiation of liver projection at the beginning
and 6 applications of vacuum ultraphoresis of the mixture
including peloidin.
It was discovered that the proposed method has led to quicker
cupping of main syndromes of the disease. The positive dynamics
of biochemical and immunological data shows the proposed
complex therapy’s efficacy. Alaninaminotransferase’s
activity level at the state of aggravation was registered
as 0.72 ± 0.03 mM and after complex restoring application
was reduced to 0.51 ± 0.05. At the stage of aggravation
the T-lymphocytes number was lowered to 42.3 ± 0.6.
After the complex restoring therapy application this number
was increased to 56.6 ± 0.9 and the suppression index
was correspondingly lowered from 4.94 ± 0.62 to 2.3
± 0.52. We have registered as well the IgA level
increase from 1.17 ± 0.02 mg/l to 1.39 ± 0.05
mg/l and IgG decrease from
12.5 ± 0.03 mg/l to 10.6 ± 0.05 mg/l. The
catamnestic survey of the children group during 2 years
showed the more prolonged stabilization of biochemical and
immunological parameters of serum.
|
|
|
F
36
ETHNOLOGICAL
STRUCTURE AND SUSCEPTIBILITY TO ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS OF
MICROORGANISMS ISOLATED FROM PATIENTS WITH URINARY TRACT
INFECTIONS
K.
Bojkova, V. Russev, V. Kaludova, V. Kamenova
Varna, Bulgaria
Objective:
To analyze the frequency and antibacterial susceptibility
of urinary pathogens in hospitalized patients.
Methods:
All urine isolates from in-patients were collected. The
analysis was based on the microbiology data. The identification
of isolates and antibacterial susceptibility test was performed
using the disk diffusion method.
Results:
We received 21 620 urine samples of which 27% fulfilled
the criteria for significant bacteriuria (pure growth of
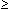 10
000 CFU/ml urine). The ten most commonly isolated microorganisms
were in decreasing order: Escherichia coli 38.17%,
Proteus spp. 9.8%, CNS 8.5%, Pseudomonas spp.
7.5%, Candida spp. 7.4%, Klebsiella spp. 7.2%,
Enterobacter spp. 6.6%, Streptococcus spp.
gr. D 6.5%, Streptococcus spp. 3.3%, S. aureus
2.3%. 10
000 CFU/ml urine). The ten most commonly isolated microorganisms
were in decreasing order: Escherichia coli 38.17%,
Proteus spp. 9.8%, CNS 8.5%, Pseudomonas spp.
7.5%, Candida spp. 7.4%, Klebsiella spp. 7.2%,
Enterobacter spp. 6.6%, Streptococcus spp.
gr. D 6.5%, Streptococcus spp. 3.3%, S. aureus
2.3%.
Escherichia coli was highly susceptible > 90%
to Cefuroxim, Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime, Gentamicin, Ciprofloxacin
and more than 80% of E. coli isolates were also sensitive
to Piperacillin, Ampicillin/Clavulanic acid, Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
and Nalidix acid. Coagulase-negative staphylococci were
predominantly susceptible to Ampicillin/Clavulanic acid
- 90%; to Oxacillin - 92%; to Ciprofloxacin - 85%. Pseudomonas
spp. presented rates of resistance as hight as 67% to
Ceftriaxone, 22% to Amikacin, 34% to Gentamicin, 26% to
Ciprofloxacin, 19% to Piperacillin. All the tested gram-positive
pathogens were susceptible to vancomycin.
Conclusion:
The most common pathogen in the area of the university hospital
among isolates from urine cultures was Escherichia coli.
Ampicillin/Clavulanic acid, Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
and Nalidix acid can be used for empiric treatment of UTI.
|
|
|
F
37
BACTERIAL
SPECTRUM IN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE
TK.
Galeas, A. Kauloumvaki, V. Galea, A. Rematisios, M. Lemoni
B' Internal Medicine Clinic, Microbiology Laboratory, General
Hospital of Trikala, Greece
The
purpose of this study was to examine the bacterial spectrum
in urinary tract infections, in elderly people, in order
to manage the most efficient therapeutic approach.
Material-method: Material of the study were 110 patients,
43 male aged 76.25 ± 7.56 and 67 female aged 75.74
± 6.02. Other 57 patients, 21 male aged 46.38 ±
15.2 and 36 female aged 46.41 ± 14.15 were the control
group. They were hospitalized in the General Hospital of
Trikala from 1/1/1993 to 20/10/1993. The patients were separated
according to gender, age and the isolated infectious factors
in urine culture. Cultures were considered positive when
concentrations of infectious factors was over 100.000/ml.
| lsolated
bacteria |
Males/aged>65
percent |
Females/aged>65
percent |
Males/aged<65
percent |
Females/aged<65
percent |
| Staphylococcus |
|
|
|
|
| E.
coli |
|
|
|
|
| Pseudomonas |
|
|
|
|
| Proteas |
|
|
|
|
| Klebsiella |
|
|
|
|
| Enterobacter |
|
|
|
|
| Mixed |
|
|
|
|
| Total
patients |
|
|
|
|
a)
Increased incidence of urinary tract infections is mostly
observed in the elderly compared with the middle aged people.
b) Isolated bacteria are observed with different frequency
in both ages, significantly in men. Most usual bacterium
is E. coli followed by staphylococcus and
pseudomonas
Conclusion:
1. Pseudomonas appears to be increased in male patients
of the third age, although it is the third cause of urinary
tract infection.
2. E coli is the main cause of urinary tract infections
in female patients of the third age.
|
|
|
F
38
POSITIVE
CULTURE OF NEGATIVE SUCTION DRAIN TIPS - A PREDICTOR OF
EARLY WOUND INFECTION?
B.
Sankar, G. Kumar, J. Rai
PGIMER, Chandigarh, lndia
Introduction:
Use of closed negative suction drain is an accepted form
of surgical wound drainage The most common source of postoperative
infection is wound contamination at surgery.
Aim:
To determine whether bacterial growth in the cultures of
drain tips and drain fluid from suction drains correlates
with early postoperative infection.
Methods
and materials: During the period April 1998 to April
1999 details of 214 consecutive clean orthopaedic operations
which needed suction drains were prospectively recorded.
The data collected included duration and number of drains
used, results of fluid and tip cultures and clinical impression
of the surgical wound in the two weeks after operation.
Results:
A total of 8 out of 214 had clinical signs of infection
within the first two weeks. Drain tips were positive in
12 cases of which 6 had positive clinical findings. Drain
fluid cultures were positive in 7 cases of which only 1
had positive clinical findings. In 1 case both cultures
were negative but had positive clinical findings of infection.
When wound infection occurred, drain tip cultures were abte
to predict this earlier by an average of 1.3 days.
Discussion:
Infection in orthopaedic surgery is a disaster. If the micro
organism(s) involved is/are identified at an earlier stage
then appropriate treatment could be instituted faster. The
results of this study show that positive culture from drain
tips can give very early indication of wound infection much
before clinical symptoms are evident.
We think that it is worthwhile to perform cultures of drain
tips in patients who are at high risk for developing post
operative wound infection.
|
|
|
F
39
INFECTIONS
AFTER INTRAORAL TUMOR SURGERY: BACTERIA AND ANTIBIOTICS
A.
W. Eckert, P. Maurer, D. Wilhelms, J. Schubert
Universitätsklinik und Poliklinik für Mund-, Kiefer-
und Plastische Gesichtschirurgie,
Institut
für Medizinische Mikrobiologie der Martin-Luther Universität
Halle-Wittenberg, Germany
Introduction:
Infections after resection of oral cancer often require
the administration of antibiotics. However, the bacterial
spectra include isolates of Enterobacteriaceae and gram-negative
aerobic Bacilli and resistance to penicillins and
cephalosporins have been described. The purpose of this
study was to determine the present bacterial spectrum and
antibiotical resistance after oral cancer surgery.
Materials
and methods: 27 patients underwent ablative tumor surgery,
in which cefotiam was parenterally admninistered from the
start of the surgery as prophylaxis. Swabs were taken from
41 clinically acute and severe infections after tumor surgery.
Additionally, all specimens of swabs were collected into
a transport media and transported to the laboratory within
24 hours.
Results:
A total of 108 bacterial strains were isolated. The ratio
between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria was 4:1. The predominant
aerobes were Enterobacteriaceae (20 isolates) followed
by Staphylococci (18 isolates) and Streptococci
(17 isolates). The majority of anaerobes were Prevotella
(8 isolates) and Fusobacterium (5 isolates).
Penicillin, Doxycyclin and Erythromycin were less active
(66%, 45% and 56% respectively). Ciprofloxacin, Cefotiam
and Piperacillin/Tazobactam showed a better efficiency,
the resistance was nearly 18%. Imipenem and Meropenem were
highly active to most of the bacteria: the resistance was
approximately 10%. In vitro Vancomycin and Teicoplanin
were still the most active of all antibiotics tested.
Conclusion:
The operative field in oral cancer surgery was colonized
by the normal oral flora and Enterobacteriaceae.
Extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) production among
members of the family Enterobacteriaceae involves
resistance to Penicillins, Cephalosporins and Monobactams
and causes serious therapeutic problems. ESBL are often
encoded by multi-resistant plasmids carrying genes conferring
resistance to other antimicrobials. Therefore, antibiotic
administration in patients who underwent oral tumor surgery
should be performed after controlling the microbiological
culture and resitogramm.
|
|
|
F
40
BACTERIOLOGY
AND ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY IN ODONTOGENIC INFECTIONS
A.
W. Eckert, P. Maurer, D. Wilhelms, J. Schubert
Universitätsklinik und Poliklinik für Mund-, Kiefer-
und Plastische Gesichtschirurgie,
Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie der Martin-Luther
Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Germany
Introduction:
Odontogenic infections are polymicrobial with a predominance
of anaerobes. With respect to the widespread resistance
in anaerobes to common antibiotics the aim of the present
investigation was to evaluate the bacterial spectra and
resistance patterns in odontogenic infections.
Materials
and methods: Pus sampies were collected from 65 patients
with acute odontogenic infections by sterile needle aspiration
immediately before incision of abscesses and/or collected
into an anaerobic transport system. All samples arrived
at the microbial laboratory within 1 hour.
Results:
65 patients (39 men and 26 women) with an odontogenic abscess
were investigated. In the "closed" odontogenic
abscess samples, a total of 226 bacterial strains were isolated;
150 (66.4%) were anaerobes and 76 (33.6%) were aerobes.
The mean number of bacterial strains per sample was 3.47.
Streptococci, Staphylococci and Neisseria
were the most common aerobic isolates. The majority of anaerobes
were Prevotella (46 isolates), Fusobacterium
(21 isolates), Eubacterium (19 isolates) and Peptostreptococcus
(16 isolates). Most of the anaerobes were highly susceptible
to Clindamycin (1.4% resistant strains), Ampicillin (2.6%
resistant strains) and Penicillin G (8.1% resistant strains).
The best antimicrobial activities showed Imipenem (0.7%
resitance), Ampicillin/Sulbactam (0% resistance) and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic
acid (0% resistance).
Conclusion:
Penicillins are still suitable for the first antimicrobial
therapy in the treatment of odontogenic infections. However,
because after beta-lactam administration increases the appearance
of beta-lactam-producing bacteria, beta-Iactam-stable antibiotics
or Clindamycin should be prescribed to this patients. The
antimicrobial efficiency of modern Fluorochinolones or Azithromycin
will be the topic of further investigations.
|
|
|
F
41
A
LEVEL OF AN ALPHA-1-PROTEININHIBITOR IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC
BRONCHITIS AND LUNG TUBERCULOSIS
M.N.
Akhtar, O.A. Dmitrikova, N.A. Zucashaevich
Department of Facultative Surgery Donetsk Medical State
University, Department of
Facultative Surgery, Ukraine
Aim:
The purpose of our research was to define a level of alpha-1-proteininhibitor
in patients with chronic bronchitis and lung tuberculosis.
Materials
and rnethods: Research of an alpha-1-proteininhibitor
level was carried out in 96 patients, suffering from a cornbination
of chronic bronchitis and lung tuberculosis. The control
group (49 persons) consisted only in patients with tuberculosis.
The basic surveyed group was subdivided into 3 subgroups
and consisted of 24 patients.
Results:
The reduction of an alpha-1-proteininhibitor level up to
a low limit have took in 3 (3.1%) patients of the first
group, in the second group - 8.9. The tuberculosis in them
was developed after 3.5. It were serious patients with emphysema
of 2-3 degree. The level of an alpha-1-proteininhibitor
in them has made 0.101, 0.15 and 0.25 mg/ml, the fraction
of an alpha-1-globulin in an albuminous spectrum of electrophotogramm
in them was reduced in 5 times, testifies about homozygous
failure. In two groups and in control of similar decrease
we have not met. An average level of an alpha-1-proteininhibitor
in 11 (50.5%) persons of the first group, 12 (23.7%) - the
second group, in 5 (20.8%) persons of the third group and
2 (6.1%) in control. In total in all surveyed groups of
average deficiency is revealed in 28 (29.1 %) patients,
corresponds to heterozygotic insufficiency. The fraction
of an alpha-1-globulin of an albuminous spectrum was reduced
in 85 cases. Increase of a level of an alpha-1-proteininhibitor
have a place in 4 (17.4%) patients of first group, 12 (42.9%)
survey of the second group, 7 (25%) persons of the third
group and 11 (29%) persons of control, that reflects intensity
of inflammatory and destructive processes in an organism.
Conclusion:
However, revealed in 3.1% patients of the first group of
low deficiency and in 28 (29.1 %) patients of moderate deficiency
of alpha-1-proteininhibitor testifies about genetically
caused inability of an organism to provide adequate protection
of pulmonary tissues from injuring influence of bacterial
and leukocytic proteinase.
|
|
|
F
42
CASE
REPORT: RECURRENT ATTACKS OF FEVER AND ABDOMINAL PAIN
R.
Gattringer
Department of Internal Medicine I, Division of Infectious
Diseases and
Chemotherapy, University of Vienna, Vienna General Hospital,
Austria
A 27
year old female patient came to the outpatient clinic with
severe abdominal pain and fever (39°C). The inflammatory
parameters were elevated: white blood count 12 G/I, C-reactive
protein 17.9 mg/dl, the blood sedimentation rate 60.
The local abdominal tenderness has been existing since one
week and started suddenly.
A short story of diagnostics and clinical course.
|
|
zurück
|