|
Various
(P 67 - P 81)
|
|
P
67
FREQUENCY
AND SENSITIVITY PATTERN OF EXTENDED SPECTRUM BETA LACTAMASE
PRODUCING ISOLATES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL LABORATORY
OF PAKISTAN
K.
Saleh
Aga Khan University, Pakistan
Objective:
To determine frequency, distribution and sensitivity pattern
of EBSL producing organism at a tertiary care hospital laboratory
in Pakistan.
Methods:
All Enterobacteriaceae isolated in a tertiary care
hospital laboratory between April and August 2002 were studied.
Isolates were speciated according to standard biochemical
tests. Susceptibility testing was performed by Kirby-Bauer
disk diffusion method. ESBL detection was done through a
double disk method using cefotaxime (30 µg) versus
cefotaxime plus clavulanate (30+10 µg) according to
NCCLS. Statistical analysis was through SPSS version 10.
Tests of significance were calculated using chi-square test.
Results:
During the 6 months study period 1137/2840 (40%) of the
isolates tested were found to be ESBL producing. ESBL positivity
was detected in 50% of Enterobacter, 41% of E.
coli and 36% of K. pneumoniae tested. ESBL production
was noted in 52% of nosocomial isolates tested (415/799).
In terms of age distribution, ESBL was more frequent in
patients at the extremes of ages (under 5 years and more
than 60 years). Furthermore cross-resistance to non-beta
lactam antibiotics (fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides and
co-trimoxazole) was also more frequent in ESBL producing
organisms (p value < 0.05).
Conclusion:
We document a high prevalence of ESBL positivity amongst
our isolates. Several laboratories in developing countries
do not routinely detect ESBL production. However, our data
supports an urgent need for regular screening and surveillance
for these organisms. Cross resistance to non-beta-lactams
agents is alarming particularly in low-income settings where
expensive second line agents are unavailable. Control of
increasing antimicrobial resistance should be included in
national health policies as a matter of priority.
|
|
|
P
68
INCIDENTAL
INTRATHECAL INFUSION OF CEFOTIAM: A CASE REPORT
G.
Brössner, K. Engelhardt, R. Beer, B. Pfausler, A. Georgopoulos,
E. Schmutzhard
Department of Neurology, University Hospital, Innsbruck,
Department of Internal Medicine I, Division of Infectious
Diseases and Chemotherapy, University of Vienna, Austria
We report
the case of a 66-year-old man with a carcinoma of unknown
primary (CUP), suffering from disseminated bone, pulmonary
and extramedullar intradural metastases, who was admitted
to the neuro intensive care unit because of massive myocloni,
spasticity of all extremities, signs and symptoms of secondary
rhabdomyolysis and increasing respiratory failure. This
lifethreatening condition most likely was triggered by an
incidental intrathecal infusion of Cefotiam (approximately
1.5 g) into an intradurally placed catheter of a pain management
system via an external pump. The level of Cefotiam in the
cerebrospinal fluid was 198.8 µg/ml (day 2) and 10.1
µg/ml (day 5). Neuroradiological (magnetic resonance
images) and neurophysiological work up (somatosensory and
motor evoked potentials) did not reveal any severe structural
or functional lesions which could have been attributed to
the intrathecal Cefotiam application. The therapeutic critical
care interventions (mechanical ventilation and hemofiltration)
and monitoring of vital parameters had to be continued for
2 weeks. Several weaning attempts – within the first
10 days – had to be stopped due to immediate reappearance
of severe myocloni. After a total of three weeks intensive
care management and monitoring the patient could be discharged
from the NICU, the neurological status having returned to
the previous condition. To the best of our knowledge, we
present the first case of an incidental intrathecal administration
of Cefotiam, showing a distinct neurological syndrome with
myocloni and secondary rhabdomyolysis, having been successfully
treated by aggressive intensive care measures.
|
|
|
P
69
PLASMA
CONCENTRATIONS OF TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR ALPHA, INTERLEUKIN-1A
AND ERYTHROPOIETIN AND THEIR RELATIONDSHIP WITH CLINICAL
OUCOME IN PATIENT WHO UNDERWENT SURGICAL INTERVENTION
S.O.
Kosulnikov, V.I. Lulko
Department of Hospital Surgery, Dnipropetrovsky State Medical
Academy, Dniepropetrovsk, Ukraine
The
problem of pathogenesis and treatment of sepsis, septic
shock, multiorgan insufficiency are discussed. The result
of clinical examination and treatment of 31 patients with
gastrointestinal stoma are presented. In 27 cases the stoma
was removed by an abdominal intervention. The investigation
employed enzyme immunoassay. Enteroanastomosis was carried
out by double-row suture and drainage of area of the anastomosis
from the perineum site by tubes for prevention of the development
of peritonitis even in case of insufficiency of the anastomosis
was made. Complications developed in 12.3% of patients,
letality made up 9.8%. Plasma cytokine concentrations fluctuate
in serious illness. We conclude that both plasma TNF-alpha
and IL-1alpha concentration often increase in sepsis and
following operative trauma. Elevated level of interleukin
1-alpha (IL-1alpha IT and tumor necrosis factor have been
increased significantly in patients before death.
The mean erythropoietin production in serum of patients
was 31.17 pg/ml compared with a control of 6.07 pg/ml. It’s
shown that optimal pathogenetic control of the inflammatory
process is possible by means of modulation of cytokine effect
and depend from individualize basal plasma levels. The level
of TNF-alpha and IL-1alpha may to be used as a marker of
prognosis for life in patients with multiorgan insufficiency
individualize.
|
|
|
P
70
IDENTIFICATION
OF A NEW PORE-FORMING OUTER MEMBRANE PROTEIN IN ACINETOBACTER
BAUMANNII.
A.
Siroy, E. Dé, D. Seyer, P. Cosette, M. Pestel-Caron,
D. Vallenet, C. Lemaître-Guillier, A. Van Dorsselaer,
T. Jouenne
Université de Rouen, Mont-St-Aignan, Faculté
de Médecine et de Pharmacie, Rouen
Génoscope, Centre National de Séquençage,
Evry, Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France
Acinetobacter
baumannii is an ubiquitous gram-negative coccobacillus
which is an important cause of nosocomial infections in
hospitals. From 1999 to 2001, multiresistant strains were
isolated during outbreaks in the emergency unit of the hospital
of Rouen (France). At this time, little is known about multidrug
resistance of A. baumannii. These resistances might
imply some alterations of the cell wall permeability. Consequently,
we investigated the outer membrane protein pattern of a
standard strain of A. baumannii (ATCC19606) as a
prelude to the study of an imipenem resistant clinical isolate.
In a first step, extraction of the bacterial cell wall and
separation of the inner from the outer membrane were performed
by ultracentrifugation on a sucrose gradient. In a second
step, we analysed by SDS and 2D-PAGE the proteic content
of the outer membrane and identified two major proteins
by mass spectrometry and N-terminal sequencing: the HMP
porin and a 29 kDa protein which had been already involved
in the imipenem resistant of another clinical isolate. Trypsic
digests of this 29 kDa protein allowed us to obtain peptidic
sequences by MALDI-TOF/TOF. By comparison with databases,
no homology was found with known membrane proteins. Purification
of this protein, using SDS-PAGE followed by electroelution
in a Triton X-100 medium, allowed us to perform functional
studies: reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers demonstrated
ion-channel forming properties for this 29 kDa protein.
|
|
|
P
71
INVASION
OF BACTERIA OF THE RESPIRATORY TRACT IN EPITHELIAL CELLS
C.
Kratzer, W. Graninger, A. Georgopoulos
Dept. of Infectious Diseases and Chemotherapy, General Hospital,
University of Vienna, Austria
Objective:
In the present study, invasiveness of 10 group A beta-hemolytic
streptococci (GAS) and 7 nontypeable Haemophili influenzae
(NTHI) were analyzed.
Methods:
All tested bacteria were clinical isolates from patients
with respiratory infections. As epithelial cells, NHBE (human
normal bronchial epithelial cells) of Clonetics and HNEpC-p
(human nasal epithelial cells) of PromoCell were used. The
uptake of bacteria in epithelial cells was evaluated by
quantifying the number of viable intracellular bacteria
recovered from epithelial cells at the end of a standard
antibiotic protection assay called internalizing or invasion
assay.
Results:
Six of the ten tested GAS throat isolates had the ability
to invade HNEpC-p cells, but they didn’t exhibit high
invasion efficiency.
Sensitive NTHI showed a total different distribution in
invasiveness in comparison to the beta-lactamase-positive
isolates. Resistant haemophili achieved an obvious higher
bacterial count within the bronchial epithelial cells than
the sensitive bacteria.
Conclusion:
For group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, no difference in
the distribution of intracellular sensitive and macrolide
antibiotics-resistant strains was found. For nontypeable
Haemophilus influenzae, it could be shown that beta-lactamase-positive
NTHI achieved good invasion in bronchial epithelial cells,
whereas sensitive strains weren’t invasive at all or
exhibited only low invasiveness.
|
|
|
P
72
RECOMBINANT
ALLERGENS PROMOTE EXPRESSION OF CD203c
A.W.
Hauswirth, P. Valent
University of Vienna, Austria
Traditionally,
the diagnosis of type I allergies is based on clinical data,
skin tests, and laboratory tests employing allergen extracts.
During the past few years several attempts have been made
to refine diagnostic assays in clinical allergy by introducing
recombinant allergens and novel markers of IgE-dependent
cell activation. We have identified the ectoenzyme CD203c
as a novel basophil antigen that is upregulated on IgE-receptor
cross-linkage. In this study, we applied CD203c and a panel
of recombinant allergens to establish a novel basophil-test
that allows for a reliable quantification of IgE-dependent
responses at the effector cell level. Patients allergic
to birch (Bet v 1, n=15; Bet v 2, n=8) and grass (Phl p
1, n=15; Phl p 2, n=10; Phl p 5, n=14) pollen allergens
as well as 10 non-allergic donors were examined. Basophils
were exposed to various concentrations of recombinant allergens
for 15 minutes and then examined for expression of CD203c
by flow cytometry. CD203c upregulation was correlated with
the increase in CD63.
Exposure to recombinant allergens resulted in a dose-dependent
increase in expression of CD203c on peripheral blood basophils
in sensitized individuals, whereas no increase was seen
in healthy controls. The effects of the recombinant allergens
on CD203c expression were also time-dependent. There was
a good correlation between allergen-induced upregulation
of CD203c and upregulation of CD63 (R=0.76).
Flow cytometric quantitation of CD203c on blood basophils
exposed to recombinant allergens is a useful approach to
determine the allergic state in sensitized individuals and
represents a basis for a sensitive novel allergo-test.
|
|
|
P
73
FUNCTIONAL
AND MORPHOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION OF DAY-10 GRANULOCYTES
IN AML PATIENTS PATIENTS RECEIVING HIDAC OR IDAC FOR CONSOLIDATION
M.T.
Krauth, S. Florian, A.W. Hauswirth, P. Samorapoompichit,
W.R. Sperr, P. Valent
Dept. of Internal Medicine I, Div. of Hematology & Hemostaseology,
University of Vienna, Austria
High
dose- (HiDAC) and intermediate dose- (IDAC) ARA-C have recently
been introduced as effective post remission treatment for
pts with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). These regimens have
been reported as a safe approach with a relatively low rate
of infections and a relatively short time of absolute neutropenia.
In this study, we analyzed the numbers, phenotype, and functional
properties of neutrophils in AML pts during consolidation
with HiDAC (n=6) or IDAC (n=6). We found that the absolute
numbers of neutrophils (ANC) remained at relatively high
levels until day 10-14. In a majority of the pts, the ANC
on day 10/11 were > 500/5l. These cells were found to
be mature neutrophils by Wright-Giemsa staining and electron
microscopy (EM). They contained secondary granules, phagosomes,
and lysosomes similar to neutrophils in healthy controls.
In addition, these cells exhibited oxidative burst activity
as assessed by the NBT test, and expressed phagocytosis-related
and activation-linked cell surface antigens including the
C3biR (CD11b), CR1 (CD35), C5aR (CD88), FcgRI (CD64), FcgRII
(CD32), FcgRIII (CD16), G-CSF-R (CD114), GM-CSF-Ra (CD116),
and sLx (CD15). The biologic significance of neutrophils
persisting until day 10 in AML pts was confirmed in functional
analyses using fluorescence labeled, heat-killed E. coli
bacteria, flow cytometry, and electron microscopy. In these
experiments, day 10 neutrophils were found to take up bacteria
into phagolysosomes in the same way as neutrophils in healthy
controls. In summary, our data show that considerable numbers
of functionally active neutrophils survive until day 10
in AML pts treated with HiDAC or IDAC. The consecutive delay
in neutropenia may be responsible for the relatively low
rate of severe infections in these pts compared to other
regimens employing high dose ARA-C in combination with other
cytostatic drugs.
|
|
|
P
74
TREATING
AN INFECTED ROTATING-HINGE ARTHROPLASTY BY A SALVAGE TOTAL
KNEE REVISION PROCEDURE – A CASE REPORT
E.
Georgopoulou, D. Kafidas, I.C. Vossinakis, L.S. Badras
Orthopaedic Department, General Hospital of Volos, Greece
Aim:
To present a complex case of infection complicating total
knee replacement.
Case
Report: A 75-year-old, obese woman with severe bilateral
knee osteoarthritis was subjected in December 1999 to a
total knee arthroplasty on her left knee.
A constrained prothesis was used due to severe deformity.
This rotating-hinge device required an extensile bone resection.
Wound dehiscence occurred, requiring reclosure.
On the 9th postoperative month she presented an established
infection along with a draining sinus. Culture swabs from
the discharge grew enterococcus sensitive to amoxicilline/clavulanic
acid. Clinical signs and infection markers responded well
to a 3-month IV antimicrobial treatment, which continued
orally for another 4 months.
In April 2001 recurrence occurred. 5 months later the prothesis
was removed and an external fixator applied. A new strain
of multiresistant enterococcus was isolated from tissue
specimens, requiring IV teicoplanine for another 3 months.
Wound healing progressed uneventfully and the fixator was
substituted by a functional knee brace.
In June 2002 revision surgery was performed, using the same
type of prothesis.
No further complications occurred so far.
Management of infection following joint replacement surgery
can be quite challenging.
|
|
|
P
75
PROCALCITONIN
AS A MARKER IN BACTERIAL INFECTIOUS DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
S.
Iacob, I. Rebedea, A. Cristescu, M. Ioan, M. Pana
Matei Bals Institute of Infectious Diseases, Bucharest,
Romania
Cantacuzino Institute
Objective:
To assess the value of procalcitonin (PCT) detection in
rapid diagnosis of different types of infections.
Methods:
Retrospective study of patients with systemic inflammatory
response syndrome (SIRS) of bacterial etiology, admitted
in Matei Bals Infectious Diseases Institute (Bucharest),
from a period of 2 years (2000-2002).
The diagnoses were based on clinical examination and paraclinical
parameters (haematologic, biochemic, and radiologic examination).
Bacterial etiology was confirmed in all patients (positive
culture of specific samples). The serum level of PCT was
measured using BRAHMS PCT-Q test in the first 10 days of
illness, before antibiotherapy.
Results:
153 patients from a total group of 230 patients with documented
SIRS were confirmed with bacterial infections (97 patients
with localized infections, 45 patients with systemic infections).The
range of PCT plasma concentrations in respect to different
bacterial infections was analyzed (tabel).
Conclusion:
In the recent years serum PCT measurement was recommended
as a possible marker of generalized and severe infections.
In our study serum PCT determination was also helpful in
localized bacterial infections (62% positivity) predominantly
in severe cases (83% positivity). All the patients with
clinical forms of tuberculosis had negative PCT.
| Diagnosis |
No.
of
patients
|
No.
of patients
with
positive PCT
|
range
of serum PCT
(ng/ml)
|
|
Localized infections |
|
|
|
1.
Bacterial pneumonia
Severe forms of
pneumonia
|
27
9
|
21
9
|
0.5-10
or >10
0.5-10 or >10
|
2.
Bacterial meningitis
Severe forms of
meningitis
|
27
6
|
21
3
|
2-10
or >10
> 10
|
| 3.
Bacterial pyelonephritis |
20
|
12
|
>
10
|
| 4.
Streptococcus pharyngitis |
20
|
8
|
>
0.5
|
| 5.
Staphylococcus cellulitis |
3
|
2
|
>
0.5
|
| 6.
Pulmonary tuberculosis |
5
|
0
|
<
0.5
|
7.
Tuberculous meningitis
|
6
|
0
|
<
0.5
|
| Systemic
infections |
|
|
|
8.
Bacterial endocarditis
Severe forms of
endocarditis |
30
6
|
11
2
|
0.5-10
or 10
> 10
|
9.
Sepsis
Severe forms of
sepsis |
15
12
|
9
6
|
0.5-10
or >10
0.5-10 or >10
|
|
|
|
P
76
INHIBITION
OF PRO- AND EUKARYOTIC TOPOISOMERASE II DNA-CLEAVAGE MEDIATED
BY MOXIFLOXACIN
B.
Körber, P. Heisig
Pharmaceutical Biology and Microbiology, University of Hamburg,
Germany
Introduction:
The bactericidal effect of fluoroquinolones results in lethal
double stranded DNA-breaks caused by stabilising bacterial
type II topoisomerase-DNA-cleavage-complexes. Due to the
enhanced clinical application of fluoroquinolone drugs and
the similarities in mechanism and structure of pro- and
eukaryotic topoisomerases II we studied the selectivities
of two modern fluoroquinolones for these enzymes by analyzing
their abilities to stabilize pro- and eukaryotic cleavage
complexes. Ciprofloxacin served as a reference.
Methods:
Fluoroquinolone mediated inhibition of prokaryotic E.
coli gyrase and eukaryotic human topoisomerase II cleavage
reaction was carried out by using a new cleavage assay protocol.
DNA-cleavage was determined as the minimum amount of moxifloxacin
(MXF), gatifloxacin (GTX) and – as a reference –
ciprofloxacin (CPX) to induce visible cleavage (i.e. 10%
= CC10) of substrate DNA.
Results:
The CC10 values of gyrase were 0.01
µg/ml, 0.05 µg/ml, and 0.005 µg/ml for
MXF, GTX, and CIP, respectively. The CC10
values of human topo II were 6 µg/ml, 2 µg/ml,
and 10 µg/ml for MXF, GTX, and CIP, respectively.
Conclusion:
Cleavage data indicate that the fluoroquinolones tested
showed drug-specific selectivity for bacterial gyrase: MXF
is 600fold and GTX 40fold more effective in stabilizing
cleavage complexes with E. coli gyrase than with
human topo II, compared to CIP (2000fold).
|
|
|
P
77
AMPLIFYING
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTION OF ANTIBIOTICS WITH THE USE OF PROTEOLYTIC
INHIBITOR AMBEN
A.S.
Fedchuk, Y.A. Boschenko, V.A. Pushkina, V.P. Lozitsky, N.N.
Man’kovskaya
I.I. Mechnikov Ukrainian Research Anti-Plague Institute,
Odessa, Ukraine
Background:
Tularemia could be used as the infectious agent during bioterroristic
attack. Cholera is treated traditionally also as the dangerous
emerging disease. The scope of the present work is the study
of the para-aminomethyl benzoic acid (Amben) influence on
the sensitivity of Francisella tularensis and Vibrio
cholerae to different antibiotics.
Methods:
We have studied the antimicrobial action of 14 representatives
of 10 antibiotics’ classes combined with Amben. Antimicrobial
susceptibility test was performed by the disk diffusion
method. Ft-agar contained 1% of Amben. Strains of Vibrio
cholerae: cholerae: strain 569 (VCC 569), El-Tor strain
754 (VCEl 754), Non-01 strain 146/11 (VCNon-01 146/11) and
virulent strain 29 of Francisella tularensis were
used.
Results:
We have discovered that all studied infectious agents are
resistant to Amben action taken apart from antibiotics.
Amben increased antimicrobial activity of gentamicin and
syzomycin against of all studied strains of Vibrio cholerae.
It has enhanced anti-cholera action of: i) cefotaxim, ofloxacin
and lomefloxacin to VCC 569 and VCNon-01146/11; ii) kanamycin
- to VCC 569 and VCEl 754; iii) norfloxacin - to VCEl 754
and VCNon 01 146/11.
Amben increased antimicrobial action of some researched
antibiotics against one strain of Vibrio cholerae.
Amben enhanced also anti-tularemia activity of tetracyclin.
Conclusion:
Analysis of the results has shown that proteolysis inhibitor
Amben increase antimicrobial efficacy of different classes
of antibiotics against various strains of Francisella
tularensis and Vibrio cholerae. Our research
has shown also that Amben could be added in certain dosage
to the antibiotics while treating the infections studied.
|
|
|
P
78
INVESTIGATION
ON IN VITRO ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF TWO BASIC SALTS OF
ZINC AND COPPER AND THEIR EFFECTS ON VIABILITY AND PROLIFERATION
OF VIRUS-TRANSFORMED CELLS
R.
Alexandrova, T. Popova, Y. Martinova, M. Gabrashanska, S.
Tepavitcharova
Institute of Experimental Pathology and Parasitology, BAS,
25 Acad. G. Bonchev Str, Sofia 1113, Bulgaria; Faculty of
Veterinary Medicine, Forest Technical University, IEMA,
IGIC, BAS, Bulgaria
The
aim of the present study was to investigate the in vitro
antimicrobial properties
of two basic salts of zinc and copper [Zn5-xCux(OH)8Cl2.H2O
and CuCO3Cu(OH)2.nH2O]
and their effects on viability and proliferation of virus-transformed
cells. The antimicrobial potential was studied on 48 gram-positive
and gram-negative bacterial strains by the routine agar-diffusion
method of Bauer-Kirby and the method of minimum inhibitory
concentrations (MIC). Both salts exhibited antimicrobial
activity in vitro although the established MICs were
higher than these of gentamicin. The cytotoxic and antiproliferative
effects of the compounds on LSR-SF-SR (established from
a transplantable sarcoma in rat induced by Rous sarcoma
virus strain Schmidt-Ruppin) and LSCC-SF-MC29 (obtained
from a transplantable chicken hepatoma induced by myelocytomatosis
virus Mc29) cell lines were evaluated. The influence on
cell viability was investigated by neutral red uptake cytotoxicity
test. The antiproliferative properties were studied using
colony-forming assay and autoradiography. CuCO3Cu(OH)2.nH2O
possessed more pronounced cytotoxic and antiproliferative
potential than Zn5-xCux(OH)8Cl2.H2O.
This salt inhibited the colony-forming ability of both cell
lines at concentrations > 0.1 mg/ml. When applied in
dose 0.1 mg/ml the compound decreased the number of LSR-SF-SR
and LSCC-SF-Mc29 labeled cells with 35% and 43%, respectively.
|
|
|
P
79
ACTIVITY
OF DISSOLVED MITOMYCIN C AFTER DIFFERENT METHODS OF LONG-TIME
STORAGE
M.
Georgopoulos, C. Vass, Z. Vatanparast, C. Pahr, A. Georgopoulos
Ophthalmology, University of Vienna, Austria
Purpose:
The cytostatic substance Mitomycin C (MMC) is used in trabeculectomy
to enhance the success rate in problematic cases and is
usually dissolved immediately before application, but only
about 1% of the substance is needed for treatment. We evaluated
different methods of long-time storage of MMC over a period
of 6 months.
Methods:
MMC (Kyowa) in concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4
mg/ml is prepared at the local pharmaceutical department
and stored at room temperature (20-24°C), at 4°C
(refrigerator), at -20°C (freezer compartment) and at
-196°C (liquid N2). The activity
of MMC is evaluated with bioassays after 30 minutes, 1,
3, 7, 14, 30, 90 and 180 days for the different concentrations
and storage methods.
Results:
There was no difference in the long-term stability of the
investigated MMC concentrations. 90% of the initial activity
was preserved after storage for 1 week at room temperature,
1 month at -20°C or 3 months at 4°C. At 6 months
the activities were 16%, 48%, and 78% of the initial values.
Conclusion:
MMC can be stored in solution for use in trabeculectomy
in the refrigerator for up to 3 months without significant
loss of activity. Storage at room temperature is not recommended.
Costs of trabeculectomy can be reduced by storage of reconstituted
solutions rather than dissolving MMC before each glaucoma-surgery.
|
|
|
P
80
LINEZOLID
IN COMBINATION WITH VANCOMYCIN AND TEICOPLANIN AGAINST MRSA
BY SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC OPTICAL DENSITY MEASUREMENTS
N.
Geisler, R. Gattringer, W. Graninger, A. Georgopoulos
Department of Internal Medicine I, Division of Infectious
Diseases and Chemotherapy, University of Vienna, Vienna,
Austria
Objective:
The Checkerboard method to assess antimicrobial combinations
is based on linear dose-response curves and therefore on
the FIC (fractional inhibitory concentration) of the tested
antimicrobial agents. Using a spectrophotometric method
for synergy experiments is a more appropriate way, because
it considers not only non-linear dose response curves, but
also shows a more kinetic view of the tested antimicrobial
combination.
Methods:
In these studies we used the BIOSCREEN C Analyzer to measure
the effects of antimicrobial combinations on the growth
rate constant of 5 strains of MRSA. Growth rate constants
were calculated from plots of the logarithm of the optical
density (OD) versus time. The growth rate constant is defined
by OD(t) = OD(0)egt. The effects
of antimicrobial combinations were assessed using increasing
concentrations of one drug plus a fixed concentration of
the other drug which leads to a 50% reduction in the value
of g compared with the control value of g (in the absence
of antimicrobial agents). The results were plotted in diagrams
by using a logarithmic scale of drug concentration on the
x-axis and the percent reduction of growth rate constant
on the y-axis. We tested Linezolid in combination with Teicoplanin
and Vancomycin, once increasing concentrations of Linezolid
combined with a fixed concentration of either Teicoplanin
or Vancomycin and then the converse experiment, with varied
concentrations of Teicoplanin/Vancomycin and a fixed concentration
of Linezolid.
Results:
Increasing concentrations of Teicoplanin and an intermediate
concentration of Linezolid showed synergy, but Linezolid
combined with the IC50 of Teicoplanin produced an autonomous
or slight additive response. Vancomycin produced an antagonistic
response when combined with Linezolid. The results were
better with the fixed concentration of Vancomycin, but showed
a large variability.
Conclusion:
The combination of Linezolid with Teicoplanin and its once
a day or even three times a week administration might be
an interesting alternative treatment of chronic osteomyelitis
or endocarditis. Another advantage would be the possibility
of outpatient therapy to save costs and prevent the spread
of resistant strains throughout the hospital during a long
stay.
|
|
|
P
81
IN
VITRO ACTIVITY OF GATIFLOXACIN AND SEVEN OTHER ANTIBIOTICS
AGAINST RESPIRATORY AND URINARY TRACT PATHOGENS FROM THE
COMMUNITY - FIRST RESULTS OF THE BASIC-STUDY
H.
Grimm
On Behalf of an European Multicenter Study Group, Institute
of Medical Microbiology, Weingarten, Germany
Objectives:
To obtain present figures on resistance against gatifloxacin
and other antibiotics.
Methods:
A total of 23 centers in Austria, Belgium, France, Germany,
Italy, Portugal, Spain and Switzerland are involved in the
BASIC study (Bacterial Annual Susceptibility Information
Collection). The MICs of gatifloxacin (Gati), ciprofloxacin
(Cipro), clarithromycin (Clari), benzylpenicillin G (Pen),
amoxicillin (Amox), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Coamox),
cefuroxime (Cur) and cefixime (Cix) were determined using
the microdilution method. Each center is requested to investigate
about 30 strains each of the following species: S. pneumoniae
(Spn), S. pyogenes (Spy), S. aureus (Sau),
E. faecalis (Efa), M. catarrhalis (Mca), H.
influenzae (Hin), E. coli (Eco), K. pneumoniae
(Kpn), P. mirabilis (Pmi) and P. aeruginosa
(Pae).
Results:
In 2001 and 2002 altogether 5,462 strains are enrolled.
Despite of any exceptions per regions some important MIC90%
/ percentage susceptible were as follows:
*) NCCLS breakpoints not available
| |
n
|
Gati
|
Cipro
|
Clari
|
Coamox
|
Cur-axetil
|
| Spn |
558
|
0.5
/ 98.9
|
2
/ - *)
|
Ž64
/ 67.7
|
1
/ 98.0
|
4
/ 79.4
|
| Hin |
580
|
0.03
/ 100
|
0.03
/ 99.8
|
16
/ 86.0
|
1
/ 95.3
|
2
/ 94.8
|
| Mca |
361
|
0.06
/ 100
|
0.06
/ 99.7
|
0.5
/ 99.2
|
0.25
/ 98.9
|
2
/ 97.8
|
| Sau |
589
|
2
/ 92.0
|
16
/ 80.5
|
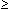 64 / 68.1
64 / 68.1 |
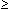 16 / 86.1
16 / 86.1 |
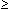 64 / 86.8
64 / 86.8 |
| Eco |
670
|
2
/ 91.3
|
1
/ 90.0
|
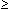 64 / - *)
64 / - *) |
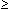 16 / 75.2
16 / 75.2 |
8
/ 95.2
|
| Pmi |
563
|
4
/ 88.6
|
2
/ 89.0
|
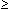 64 / - *)
64 / - *) |
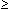 16 / 87.6
16 / 87.6 |
32
/ 85.6
|
| Pae |
569
|
16
/ 72.1
|
16
/ 76.3
|
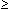 64 / - *)
64 / - *) |
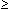 16 / - *)
16 / - *) |
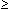 64 / - *)
64 / - *) |
Conclusion:
From the oral antibiotics tested gatifloxacin has the highest
activity and broadest spectrum against all relevant respiratory
and urinary tract pathogens. Gatifloxacin is a promising
alternative for therapy of respiratory and urinary tract
bacterial infections.
|
|
zurück
|